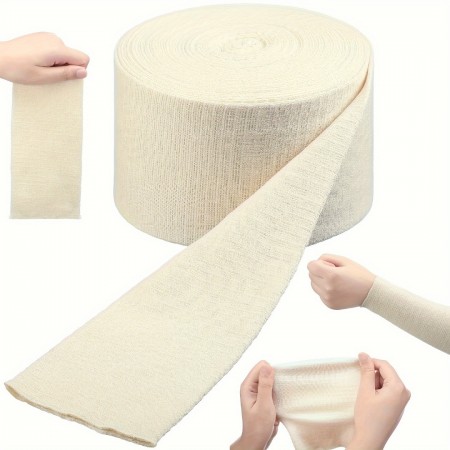
Protection: Surgical bandages provide a protective barrier for wounds and surgical sites. They shield the affected area from external contaminants, reducing the risk of infection and promoting a cleaner healing environment.
Support: These bandages can offer support to injured or operated areas, helping to stabilize the tissue and reduce movement that could impede healing or cause further damage. This is particularly important for areas like joints or the abdomen.
Absorption: Many surgical bandages are designed with absorbent materials that can manage exudate (fluids from the wound). This absorption helps keep the wound dry, which is essential for proper healing and can prevent maceration of the skin around the wound.
Comfort: Surgical bandages are often made with soft, breathable materials that are gentle on the skin and do not cause irritation. They are designed to be comfortable for the patient, allowing for prolonged wear without discomfort.
Visualization: Some surgical bandages are transparent or have windows that allow healthcare providers to visually inspect the wound without removing the bandage entirely. This feature is crucial for monitoring the healing progress and identifying any signs of complications early.
Ease of Application and Removal: Surgical bandages are typically designed to be easy to apply and remove, reducing the risk of disturbing the wound during changes. This ease also contributes to the overall comfort and convenience for both patients and healthcare providers.
Customization: There are various types of surgical bandages available, ranging from simple adhesive strips to more complex multi-layer bandaging systems. This variety allows for customization based on the type and stage of the wound, ensuring that the bandage meets the specific needs of the patient and the healing process.