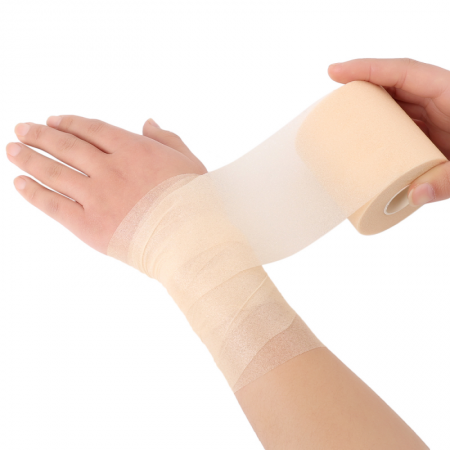
Protection Against Infection: Surgical bandages are designed to create a sterile barrier that helps prevent bacteria and other pathogens from entering the wound site. This barrier is crucial for reducing the risk of infection, which is a major concern following surgical procedures.
Supports Healing: These bandages often incorporate materials that help maintain a moist environment around the wound, which is known to promote faster and more effective healing. The moisture-retaining properties of surgical bandages can help keep the wound bed hydrated, aiding in the regeneration of healthy tissue.
Customizable and Versatile: Surgical bandages come in various forms, such as gauze pads, wraps, and adhesive strips, allowing for customization based on the specific needs of the wound. This versatility means that they can be adapted to fit different wound sizes and locations, ensuring that the bandage stays in place and provides optimal coverage.
Comfort and Flexibility: Designed with patient comfort in mind, surgical bandages are often made from soft, breathable materials that allow the skin to breathe while also being flexible enough to accommodate movement. This flexibility is particularly important for wounds located in areas where the skin stretches or bends, such as joints.
Secure Adherence: Surgical bandages are engineered to adhere securely to the skin without causing damage upon removal. This secure attachment helps prevent the bandage from shifting or falling off prematurely, which could compromise the healing process and expose the wound to contaminants.
Ease of Use and Application: Surgical bandages are typically easy to apply and remove, making them convenient for both medical professionals and patients. They are designed to stay in place without the need for frequent adjustments, which can be beneficial for patients who need to manage their own wound care at home.